


On rare occasions, WISE data exhibit an interesting phenomenon whose nature is unknown. A large annulus of W2 pixels, centered roughly on the pixel at coordinates [912,568] (0-indexed, as in IDL) and hereafter referred to as the "resonant pixel," appears then subsequently decays in later frames. This halo is usually preceded by a dramatic elevation of signal, colloquially referred to as a "TV test pattern" (also of unknown origin), that appears in both W1 and W2. The phenomenon is often accompanied by a W1 latent at approximately the same row as the W2 resonant pixel halo, but on the left side of the array. This W1 latent is generally present in strong instances of the W2 phenomenon.
The following figures illustrate, in chronological order, the fifty-two recorded instances of the W2 resonant pixel phenomenon. In all figures, each row represents a simultaneously taken set of frames that, from left to right, represent W1, W2, W3, W4, and a three-color image formed using the W1+W2(+W3+W4) frames. The frame number in the scan is shown to the far left. Icons with open white squares or question marks indicate missing bands of data. For example, data taken during the NEOWISE Reactivation period lack W3 and W4 data.
The first instance of the resonant pixel phenomenon occurred during the WISE 4-band cryogenic period (Figure 1), followed by one instance in the WISE 3-band cryogenic period (Figure 2), three instances during the WISE post-cryogenic period (Figures 3-5), and forty-seven instances during NEOWISE reactivation (Figures 6-52).
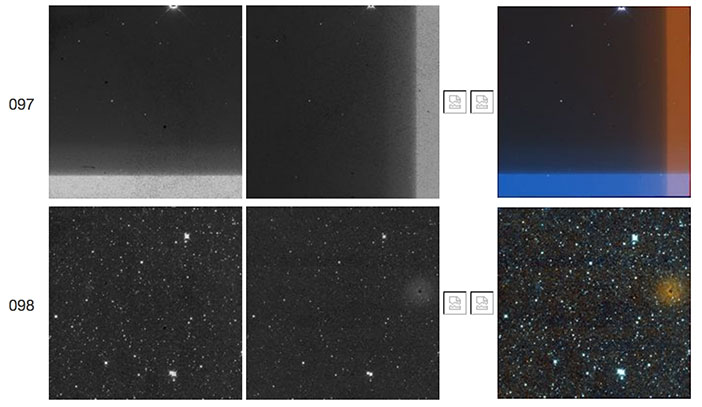 |
| Figure 7 - Scan 67842b, framesets 097-098. Frameset 097 exhibits a "TV test pattern". Frameset 098 shows a weak W2 resonant pixel halo. |
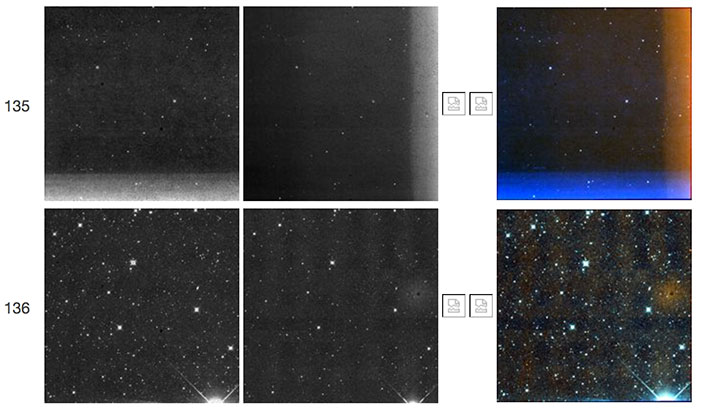 |
| Figure 9 - Scan 73648a, framesets 135-136. Like Figures 7 and 8 above, the first frameset shows a "TV test pattern" followed in the second frameset by a weak W2 resonant pixel halo. |
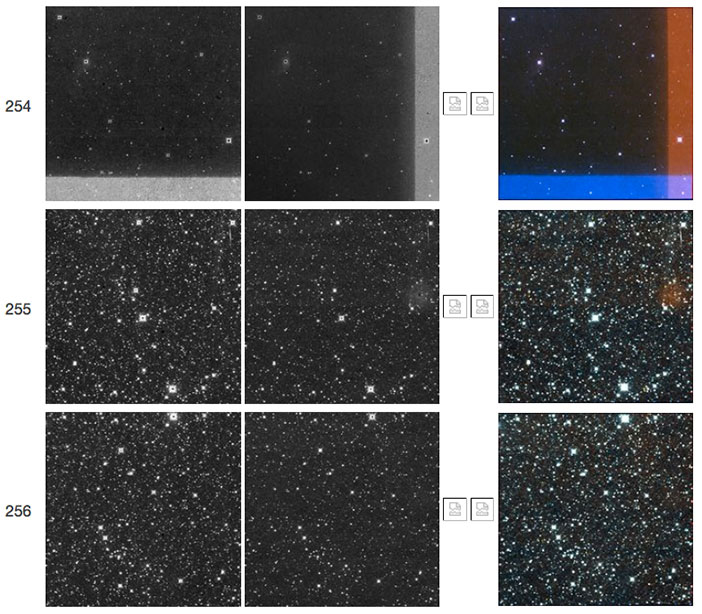 |
| Figure 11 - Scan 77978a, framesets 254-256. The first frameset shows a "TV test pattern" followed in subsequent framesets by a W2 resonant pixel halo. |
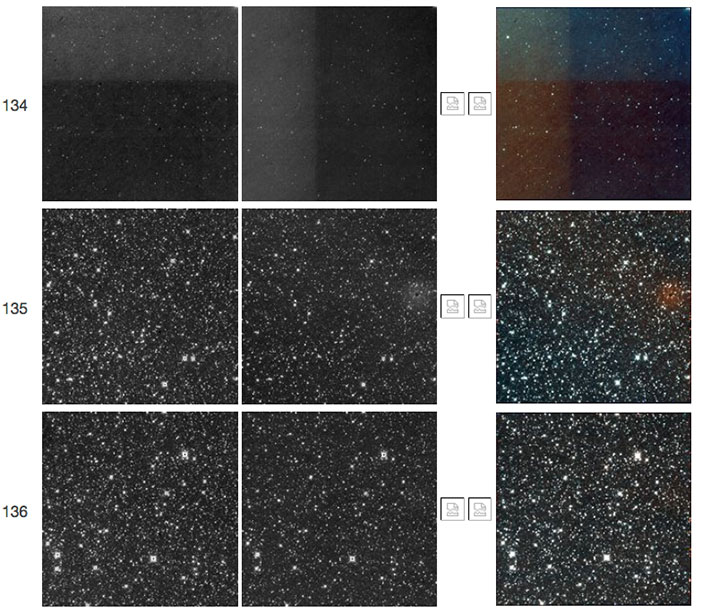 |
| Figure 13 - Scan 79980a, framesets 134-136. The first frameset shows a "TV test pattern" followed in subsequent framesets by a W2 resonant pixel halo. |
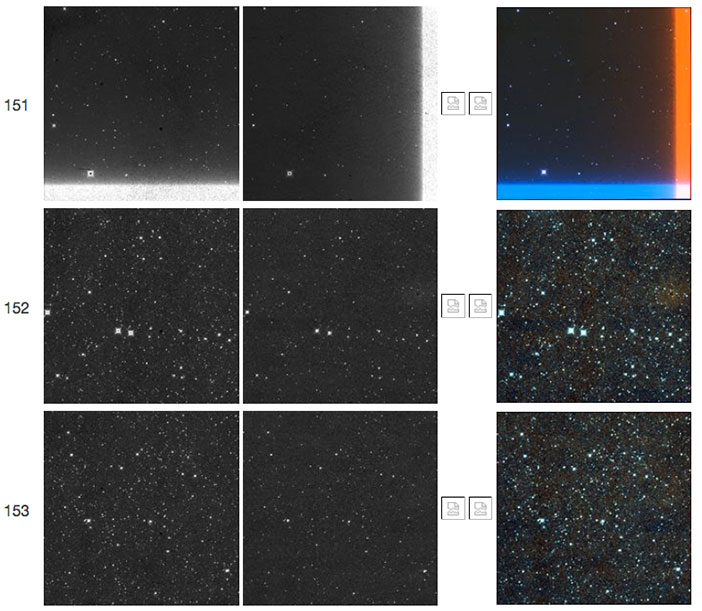 |
| Figure 16 - Scan 82157b, framesets 151-153. The first frameset shows a "TV test pattern" followed in subsequent framesets by a W2 resonant pixel halo. |
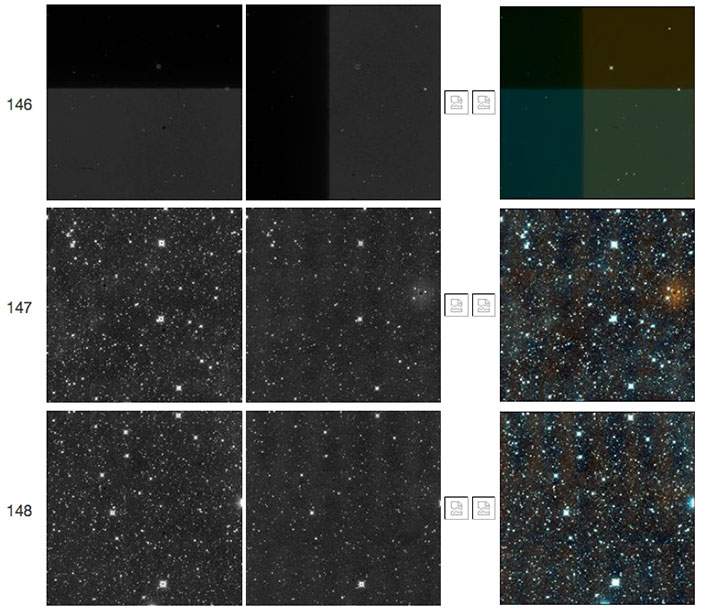 |
| Figure 17 - Scan 84826a, framesets 146-148. The first frameset shows a "TV test pattern" followed in subsequent framesets by a W2 resonant pixel halo. |
 |
| Figure 21 - Scan 91539a, framesets 187-188. The first frameset shows a "TV test pattern" followed in the subsequent frameset by a W2 resonant pixel halo. |
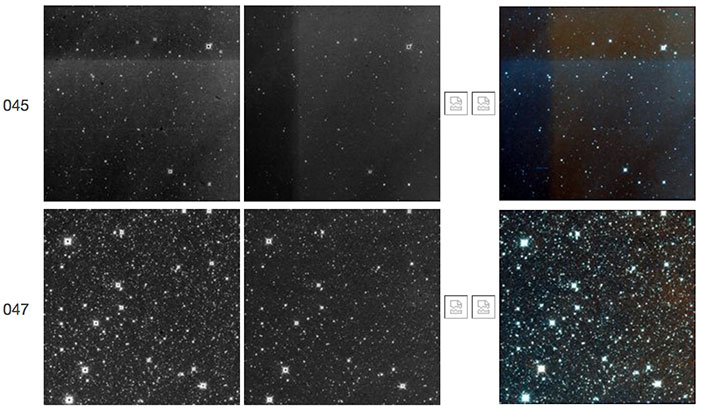 |
| Figure 28 - Scan 05932r, framesets 045-047. The first frameset shows a "TV test pattern" followed in the second frameset by a very weak W2 resonant pixel halo. |
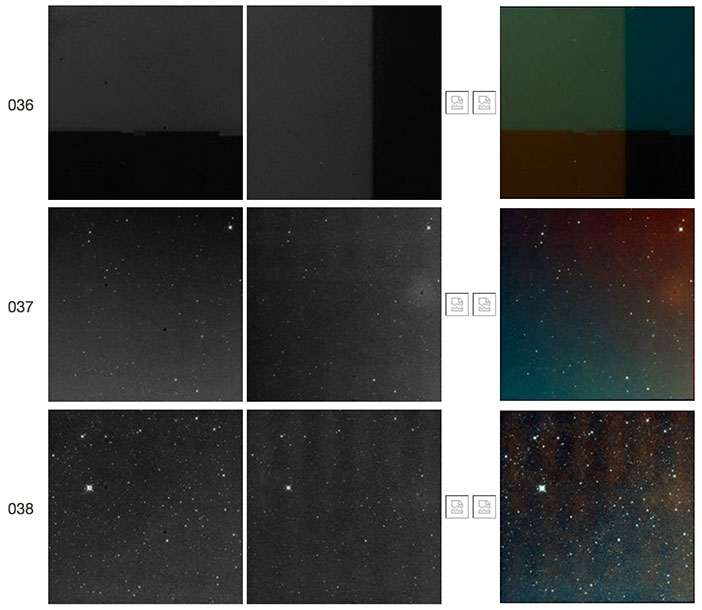 |
| Figure 30 - Scan 11960r, framesets 036-038. The first frameset shows a "TV test pattern" followed in the next two framesets by a decaying W2 resonant pixel halo. |
 |
| Figure 52 - Scan 62217r, framesets 027-028. The first frameset shows a "TV test pattern" followed in the next frameset by a weak W2 resonant pixel halo. |
Figures 53 and 54 show 31×31 pixel cut-outs centered at the nominal resonant pixel, for each of the first framesets in Figures 1-10 that show the feature. These cut-outs are shown in the two Figures 53 and 54, instead of a single figure, for clarity. The resonant pixel seems to have very low responsivity, but is also transient. Pixels in its vicinity are also transient, are excessively noisy, or have very low responsivity. Note that dead pixels have constant signal at the digital saturation level. The figures show that the nominal resonant pixel itself is not unique but more likely is a member of a tight cluster of masked pixels. Color coding on the figures is explained in the legend below:
Table 1: Color Coding of Masked Pixels
|
|
Excessively noisy, or known broken hardware. Static mask |
|
|
Dead, or low responsivity or low dark current. Static mask |
|
|
High dark current or responsivity, or saturated at any sample, or uncertain non-linearity. Static mask |
|
|
Broken pixel, or negative slope fit. Dynamic mask |
|
|
Saturated at any sample. Dynamic mask |
|
|
Transient, or unreliable non-linearity, or spike outlier. Dynamic mask |
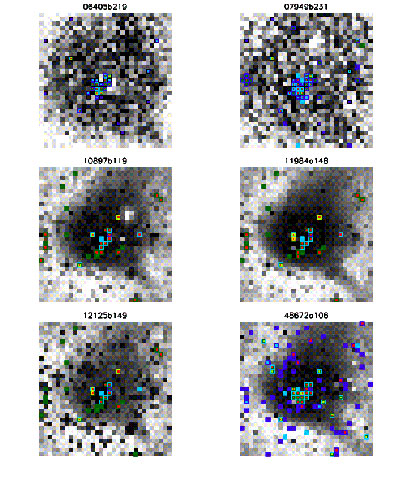 |
| Figure 53 - Zoom-ins centered at the resonant pixel feature from Figures 1-6. See Table 1 for an explanation of the color coding of masked pixels. |
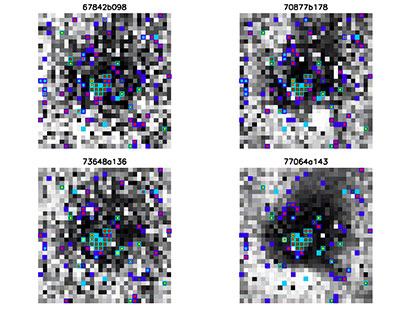 |
| Figure 54 - Zoom-ins centered at the resonant pixel feature from Figures 7-10. See Table 1 for an explanation of the color coding of masked pixels. |
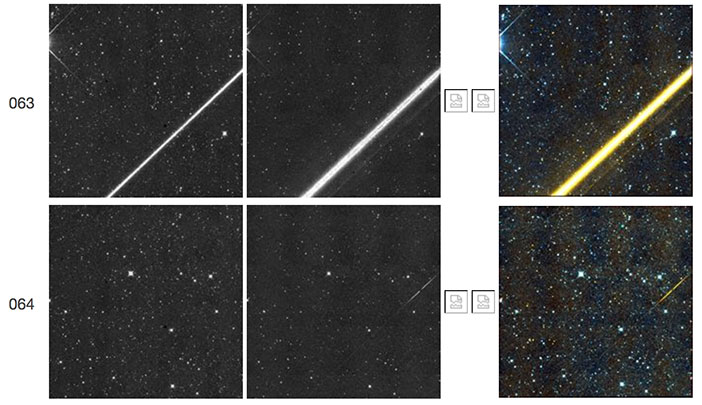
It has been observed that bright objects falling near the right edge of the W2 array tend to produce longer-lasting latents than bright objects falling elsewhere, as discussed in IV.4.g.iv.1.e. Figure 55 shows an example of this effect. The bright satellite trail in this figure leaves a W2 latent but only in the vicinity of the resonant pixel. Figures 56 and 57 show similar instances where brighter satellite trails leave W2 latents in the subsequent three or four framesets, but markedly brighter at the resonant pixel position. That the resonant pixel falls within this region, where bright stars and satellite trails leave more prominent latents than elsewhere in the array, suggests that the two effects may be related. This point is further illustrated in Figures 58 and 59, which are zoomed versions of satellite trails and of the resonant pixel.
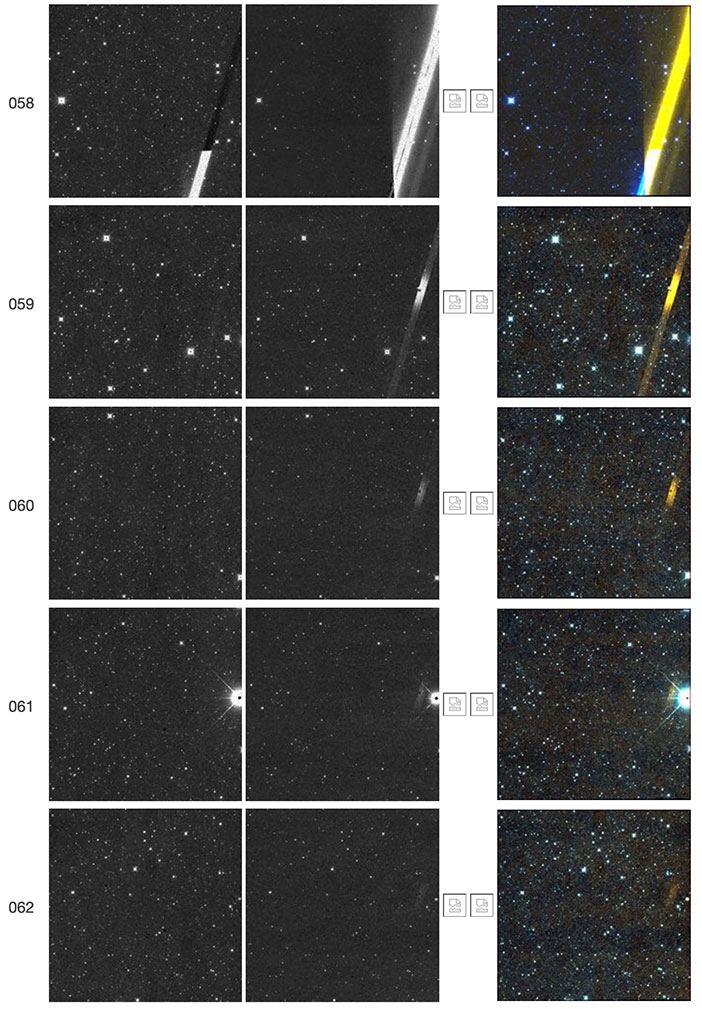 |
| Figure 56 - Scan 57227r, framesets 058-062. The bright satellite trail in frameset 058 leaves W2 latents in framesets 059-062. These latents are pronouncedly brighter at the position of the W2 resonant pixel, thus further suggesting that the latter is related to the phenomenon of longer-duration short-term latents in this region of the array. |
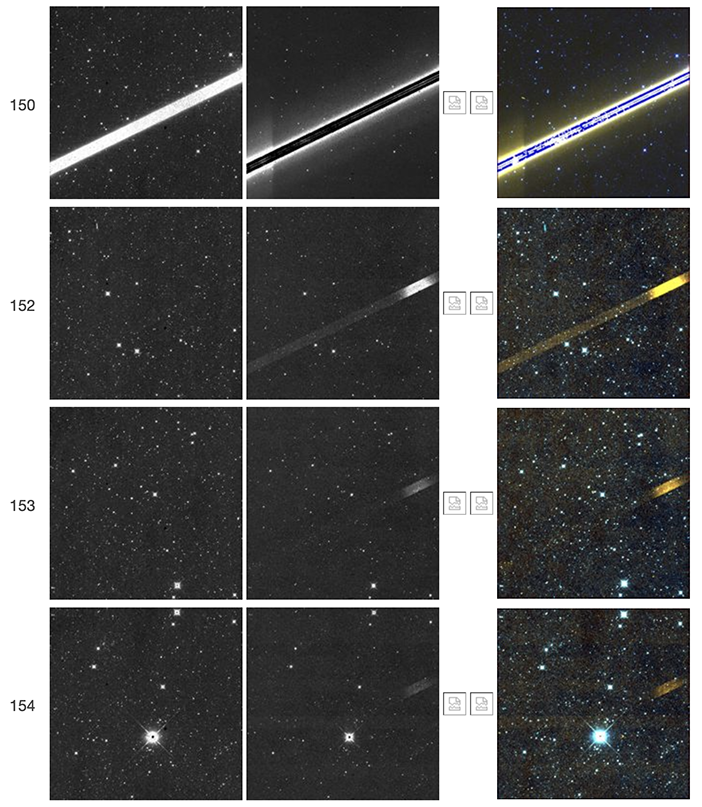 |
| Figure 57 - Scan 61073r, framesets 150-154. This is another example of a bright satellite trail, in this case in frameset 150, that coincidentally crosses the W2 resonant pixel. It leaves W2 latents in framesets 152-154, which, as in the case of Figures 55 and 56, are pronouncedly brighter at the position of the W2 resonant pixel. This example further suggests that the W2 resonant pixel is related to the phenomenon of longer-duration short-term latents in this region of the array. |
We looked for a correlation between the intensity of the resonant pixel feature, and the signal in the illuminated frameset preceding it. To this end, we carried out aperture photometry with the ATV tool in IDL, centered at the nominal resonant pixel position, and using the radii for aperture and sky annuli illustrated in Figure 60. We separately calculated the centroid of the feature, via its first moment of inertia, and found out that it is reasonably constant, except for the faintest examples that are affected by noise.
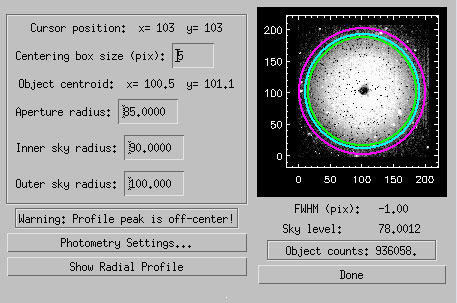 |
| Figure 60 - GUI for ATV photometry centered at the resonant pixel position, illustrated for frameset 148 in scan 11984a. |
Table 2 lists our measurements for all the fifty-two instances of the resonant pixel. We obtained the mean signal of the illuminated W2 frame (the one for which the frameset often shows a "TV test pattern"), except for the framesets in Figures 1, 2, 4, 6, 14, 24, 29, 34, 37, and 43 for which there were no level-1b data available for the illuminated W2 frame. In cases where a TV test pattern was discernible, we also measured the W2 signal jump between the elevated region and the rest of the array. Figure 61 illustrates an example estimate of signal jump in a TV test pattern. We also measured the signal at the top of either the TV test pattern (row cut in the right-hand-side panel of Figure 61) or the maximum signal of the illuminated W2 frame. We also measure aperture photometry of the resonant pixel feature, except for the framesets in Figures 9, 16, 26, 30, 34, 37, 38, 50, and 52 for which this feature is either too faint (in most cases), or is contaminated by sources or cosmic rays (such as in the case of Figures 50 and 52).
Table 2: Measured Signal in the Resonant Pixel Halo and in the Preceding Frame
|
Figure |
Aperture Photometry of Resonant Pixel (DN) |
Mean Signal In Preceding Illuminated W2 Frame (DN) |
W2 Signal Jump In TV Test pattern (if visible) (DN) |
Maximum Signal In Preceding Illuminated W2 Frame (DN) |
Resonant "Pixel" Feature Centroid (pix) |
|
1 |
430,132 |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
[912.7, 567.3] |
|
2 |
80,263 |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
[912.7, 567.3] |
|
3 |
647,687 |
224.6 |
6,300 |
7,500 |
[911.9, 567.5] |
|
4 |
936,058 |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
[912.2, 567.7] |
|
5 |
241,604 |
10,982 |
N/A |
11,500 |
[912.3, 567.5] |
|
6 |
634,134 |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
[912.5, 567.4] |
|
7 |
64,177 |
401.9 |
900 |
1,200 |
[912.4, 567.2] |
|
8 |
99,804 |
96.88 |
230 |
380 |
[912.3, 567.1] |
|
9 |
< 0 |
1,324 |
400 |
1,800 |
[912.0, 567.0] |
|
10 |
267,156 |
11,050 |
1,300 |
11,300 |
[911.6, 563.7] |
|
11 |
258,044 |
2,527 |
700 |
3,100 |
[914.0, 556.7] |
|
12 |
48,953 |
532.6 |
1,200 |
1,400 |
[908.6, 564.5] |
|
13 |
200,573 |
5,128 |
300 |
5,400 |
[912.3, 566.0] |
|
14 |
698,415 |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
[912.9, 568.8] |
|
15 |
41,645 |
50.6 |
10 |
50 |
[912.9, 567.2] |
|
16 |
< 0 |
144.6 |
460 |
575 |
[911.9, 567.1] |
|
17 |
150,387 |
900 |
1,200 |
1,450 |
[911.2, 567.2] |
|
18 |
80,692 |
2,929 |
280 |
2,750 |
[912.3, 567.4] |
|
19 |
276,330 |
2,391 |
7,790 |
7,800 |
[913.2, 567.4] |
|
20 |
148,969 |
448 |
2,050 |
2,200 |
[912.6, 567.0] |
|
21 |
111,000 |
739 |
900 |
1,250 |
[912.2, 566.2] |
|
22 |
49,065 |
730 |
815 |
875 |
[908.4, 564.0] |
|
23 |
80,731 |
1,878 |
800 |
2,000 |
[913.4, 567.4] |
|
24 |
852,538 |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
[913.2, 566.2] |
|
25 |
57,570 |
1,682 |
2,200 |
2,250 |
[913.1, 566.2] |
|
26 |
< 0 |
2,098 |
150 |
2,250 |
[912.8, 567.1] |
|
27 |
27,759 |
893 |
220 |
1,050 |
[911.2, 568.0] |
|
28 |
67,389 |
1,055 |
170 |
1,620 |
[912.8, 568.1] |
|
29 |
943,310 |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
[912.5, 567.0] |
|
30 |
< 0 |
5,645 |
1,500 |
6,300 |
[912.9, 567.2] |
|
31 |
242,873 |
5,446 |
500 |
5,650 |
[914.0, 564.9] |
|
32 |
202,935 |
4,070 |
800 |
4,150 |
[912.1, 566.1] |
|
33 |
159,364 |
2,952 |
2,050 |
4,500 |
[912.3, 567.1] |
|
34 |
< 0 |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
[912.5, 567.0] |
|
35 |
242,648 |
4,494 |
1,600 |
4,700 |
[911.8, 568.2] |
|
36 |
552,186 |
274 |
160 |
380 |
[912.6, 569.6] |
|
37 |
< 0 |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
[912.5, 567.1] |
|
38 |
< 0 |
684 |
125 |
775 |
[912.7, 566.9] |
|
39 |
119,262 |
3,048 |
700 |
3,450 |
[912.3, 567.4] |
|
40 |
262,575 |
154 |
N/A |
450 |
[912.5, 567.8] |
|
41 |
5,997 |
1,017 |
100 |
1,200 |
[912.0, 566.9] |
|
42 |
320,699 |
10,521 |
800 |
11,000 |
[912.1, 567.0] |
|
43 |
701,452 |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
[912.4, 567.3] |
|
44 |
65,678 |
786 |
1,025 |
1,150 |
[911.8, 566.4] |
|
45 |
86,851 |
996 |
1,050 |
1,250 |
[912.8, 567.6] |
|
46 |
164,764 |
1,142 |
2,200 |
2,550 |
[912.3, 567.2] |
|
47 |
41,781 |
888 |
1,005 |
1,075 |
[913.3, 562.5] |
|
48 |
116,580 |
4,537 |
1,000 |
4,900 |
[913.1, 566.9] |
|
49 |
758,146 |
8,633 |
4,650 |
10,750 |
[909.1, 566.2] |
|
50 |
N/A |
490 |
N/A |
500 |
[912.9, 566.6] |
|
51 |
55,831 |
1,942 |
975 |
1,375 |
[912.3, 567.2] |
|
52 |
N/A |
1,006 |
550 |
1,350 |
[911.8, 563.6] |
Figure 62 shows the mean and maximum signal of the preceding illuminated W2 frame, and the signal jump in the TV test pattern, as a function of aperture photometry of the W2 resonant pixel halo. Figure 62 shows that there is a correlation between the signal in the resonant pixel halo and the maximum signal in the preceding frame (red symbols). This correlation is weaker for the mean signal of the preceding frameset (blue circles), and even weaker for the signal jump in the TV test pattern (green circles).
The resonant pixel halo is related not to a single pixel, but to a cluster of them in W2, and it is located in a region of the array where long-term latents are observed. Instances are rare and are preceded by a frameset with a dramatically elevated signal, often with a "TV test pattern" effect.
Last update: 12 November 2024


