


V. AllWISE Data Processing
1. Overview
Science data processing for AllWISE program was carried out using
elements of the WISE Science Data System (WSDS)
that was developed and operated at the Infrared Processing and
Analysis Center, California Institute of Technology.
AllWISE utilized the WSDS Multiframe Pipeline,
QA and Archive elements, augmented with new
functionality to support
the objectives of AllWISE, and improved to address some known
deficiencies known to exist in the earlier WISE data products.
The many significant updates to the WSDS for AllWISE processing are
summarized in V.1.a.i below.
As described in V.1.b, AllWISE makes use of the
W1 and W2 Single-exposure images from the WISE
4-Band,
3-Band Cryo and
NEOWISE Post-Cryo survey phases,
and the W3 and W4 Single-exposure images from the 4-Band Cryo survey phase.
Key improvements were made to pixel calibrations
and astrometric solutions for the Single-exposures
to improve the overall quality of the AllWISE Data products.
These improvements are described in
V.2.a and V.2.b.
V.1.a. The Multiframe Pipeline
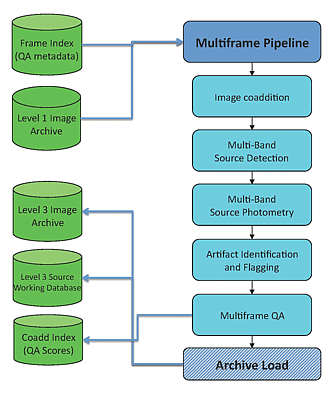 |
| Figure 1 - The WSDS Multiframe Pipeline operational processing
flow |
Core data processing for AllWISE used the WSDS Multiframe Pipeline.
The elements of the Multiframe Pipeline are
shown above in Figure 1.
The Multiframe Pipeline takes as input the Single-exposure
images and metadata that were originally produced by the
Scan/Frame pipeline,
and improved for AllWISE as described in V.2.a and
V.2.b.
The AllWISE Multiframe processing steps are:
- Image coaddition - Single-exposure frame images that
satisfy minimum quality criteria (V.1.b) are
match-filtered, registered and combined on pre-defined
Atlas Tile
footprints on the sky in the Atlas Image generation step
(V.3.a).
Throughput matching is performed to adjust for data from the different
survey phases, and pixel outlier rejection suppresses transient features
and fast moving objects.
- Multiband Source Detection - Sources are detected
simultaneously in the four WISE bands on a combined signal-to-noise image
formed from the four-band coadded images in the MDET source detection step
(V.3.b.i).
- Source Extraction - Positions, apparent motion and
photometry for each detected source are measured in the WPHOT subsystem
(V.3.b.ii).
Profile-fit photometry is performed simultaneously in four bands
and on all Single-exposure framesets to produce
one set of calibrated magnitudes per object. Profile-fit fluxes for
each detection are are also measured on the individual Single-exposure
framesets and output to the
Multiepoch Photometry Database.
A variety of aperture photometry measurements are performed for each object
on the coadded Atlas Images, including
special elliptical aperture measurements for sources identified
with galaxies in the 2MASS Extended Source Catalog.
- Artifact Flagging - Source extractions that may be
contaminated by or spurious detections of image artifacts produced by
bright sources are identified and tagged in the ARTID subsystem
(V.3.d).
- QA - Coadd image and extracted source quality is assessed
by the Multiframe Quality Assurance operation
(IV.6.iii).
Performance metrics are generated by each Multiframe pipeline subsystem and
general pipeline output, and reviewed by quality assurance scientists
to identify anomalies. The QA system assigns a numerical quality
score to the Multiframe pipeline output for each Atlas Tile.
- Archive Loading - Output from the Multiframe Pipeline,
including the coadded Atlas Image sets, Source Working Database and
metadata information
are loaded into the WISE data archive within IPAC's NASA/Infrared Science Archive (IRSA) following completion
of Multiframe processing and quality assessment. The elements of the
Archive system are described in
section IV.7 of the WISE All-Sky Release Explanatory
Supplement.
The basic astrometric and photometric calibration information in the
individual Single-exposure images was propagated to the coadded images Atlas
and deep source extractions during the Multiframe processing.
Small adjustments were applied to the Single-exposure
WCS information and
photometric zero points during
the image coaddition step to take advantage of improvements generated for
AllWISE.
Pixel values of the individual Single-exposure images are
scaled so that all AllWISE Atlas Images
have the same photometric zero point within a band.
AllWISE Multiframe Pipeline processing generated
18,240 Atlas Image sets
covering the sky, a deep-detection Working Database containing
1,176,421,279 source extractions, the
42,759,337,365 entry
Multiepoch Photometry Database,
and associated metadata products. The Working Database
is split into the Source Catalog
and Reject Table
during the Catalog Generation step.
V.1.a.i. Synopsis of the WSDS Improvements for AllWISE
V.1.a.i.1. Added Functionality
- Update WSDS and Multiframe Pipeline infrastructure to manage and combine
data from all survey phases. See V.1.b.
- Introduce small, linear motion term to PSF-fit measurement model.
See V.3.b.ii.
- Output the Single-exposure photometric measurements forced at
the position of each deep-detection for the Multiepoch Photometry
Database. See V.3.b.v.
V.1.a.i.2 Single-exposure Updates
- Apply new instrumental calibrations to remove spike in pixel
histograms that contributed to local background level overestimation,
and subsequent
source flux overestimation.
See V.2.a.
- Derive updated WCS information for each Single-exposure frameset
by correcting for 2MASS astrometric reference star proper motions in
the 11 years separating the 2MASS and WISE surveys, and by using
the repeated observations of sources in WISE frameset overlaps.
See V.2.b.
V.1.a.i.3. Improved Calibrations
- Finer resolution to photometric instrumental zero points to
track rapidly changing system throughput during the 3-Band and
Post-Cryo survey phases. See V.3.e.
- Static correction of 0.011 mag to W1 photometric instrumental zero point
for the 4-Band Cryo measurements. See V.3.e.
V.1.a.4. Improved Reduction Algorithms
- Image Coadder (see V.3.a)
- Utilize updated frameset WCS information.
- Apply photometric zero point offset refinements
- Implement hard saturated pixel flag masking (engendering the
problem where the early 3-Band Cryo W1 were saturated)
- Expand saturated pixel regions to better handle detection and
extraction of very bright sources.
- Expand the W2 scattered moonlight mask
- Make W2 dynamic frame filtering more aggressive to exclude more frames
affected by scattered moonlight.
- Tune pixel outlier rejection algorithm to better handle disparate
behavior of imaging from the three WISE survey phases.
- Compute the mean offsets between flux-weighted source centroids
measured on Atlas Images and Source Catalog positions.
- Source Detection and Extraction (see V.3.b).
- Lower source detection threshold SNR to 2.4.
- Improve initial detection brightness estimates for input to
source extraction.
- Improved masking of saturated pixels around very bright sources
to compensate for reduced effectiveness of payload saturation encoding
in the 3-Band and Post-Cryo phases.
- Optimize handling of groups of detections in close proximity to
improve processing throughput.
- Improved accuracy and robustness of local background estimation
algorithms for source photometry.
- Made local background estimates consistent for PSF-fit and aperture
photometry.
- Corrected error that produced bimodal Single-exposure photometric
uncertainties (for Multiepoch Photometry Database).
- Updated and added Single-exposure flux measurement distribution
statistics for improved flux variability identification and
classification.
- Updated 2MASS XSC source size scaling for extended source flagging,
and included flagging for smaller 2MASS XSC sources.
- Identified and classified small-separation, same-Tile duplicate sources.
See V.4.
- Astrometry (see V.3.c)
- Improved band-frame pixel alignment for coaddition.
- Align AllWISE astrometry with the inertial 2MASS reference frame.
- Improved proper motion-corrected astrometry cross checks with
the UCAC4 catalog.
- Artifact Identification (see V.3.d)
- Improved depth-of-coverage scaling for off-Tile bright parent
sources.
- Improved parent star brightness estimates when measured brightnesses
are upper limits.
- Quality Assurance
- Added apparent motion measurement quality metrics, diagnostic plots
and images.
- Evaluated quality of significant motion measurements for trending
and classification.
- Catalog Generation (see V.4)
- Add small-separation, same-Tile duplicate handling in duplicate
source generation.
- Update Catalog source selection criteria.
- Archive
- Load, manage and build interfaces for the very large Multiepoch
Photometry Database.
- Improved loading efficiency for all database tables.
- Add level 20 HTM spatial indexing in all database tables to improve
query performance.
V.1.a.ii. Basic Data Processing Terminology
orbit - An orbit refers to the observations or block of
survey data acquired between the times WISE observed the north ecliptic pole
(NEP). The WISE orbital period is approximately 95.3 minutes.
Orbit number 1 was defined to start with the fictitious
NEP passage immediately prior to WISE launch. Thus, WISE was launched
into orbit #1. The AllWISE Products are made from data taken
from the start of full cryogenic survey observations in orbit
356 to the point at which data acquisition was halted
in orbit 6257.
scan - A scan refers to the observations or block of survey
imaging data acquired between two flight system maneuvers, such
as reorientation of the instrument boresight near the ecliptic poles,
or slews to acquire TDRSS for data downlink contacts. Because
maneuvers often took place near the ecliptic poles, a scan
is associated with the image data from approximately a half-orbit. However,
scans can cover less or more than half of the arc between ecliptic
poles. Scans are identified in the Single-exposure image headers,
Single-exposure source database and metadata tables by the
scan_id.
single-exposure - Single-exposure refers to the unit of
data acquisition carried out by WISE while the sky is frozen onto the
focal plane detectors, and to the set of imaging data collected
during this data collection.
frame - A frame is the image data acquired in a single band from
a WISE Single-exposure. A Single-exposure was acquired approximately
every 11 seconds during WISE scans. The frame exposure times are 7.7 sec in
W1 and W2 and 8.8 sec in W3 and W4. Because scans have different
lengths, the number of frame exposures acquired per scan varies.
A histogram showing the distribution of the number of frames per scan
for all WISE survey scans is shown in Figure 2.
frameset - The set of 1-4 images (frames), one in each band
(W1, W2, W3, W4), that are acquired simultaneously during each WISE
single-exposure. The same region of sky is imaged in all bands.
WISE collected images in all four bands during the
4-Band Cryo phase,
W1, W2 and W2 during the 3-Band Cryo phase,
and W1 and W2 during the Post-Cryo phase.
coadd - Image data in a single band produced by combining
multiple Single-exposure frames that cover the same region of the sky.
Coadds are produced in the Multiframe pipeline by
resampling, reprojecting and coadding single-exposure frames onto predefined
spatial footprints.
coaddset - The set of four corresponding coadds, one in each
WISE band (W1, W2, W3, W4), that are generated by combining multiple framesets.
Coaddsets are generated by the
Multiframe pipeline.
Atlas Tiles - A
predefined grid
of 18,240 regions on the sky onto which coaddsets are generated by the
Multiframe pipeline for AllWISE data release products.
Atlas Tiles cover 1.564°x1.564° (4095x4095 pix @1.375"/pix)
and are built on an equatorial projection.
Atlas Image - An Atlas Image is the particular case of
a coadd image built on the footprint of an Atlas Tile. The AllWISE
coadd intensity images are Atlas Images.
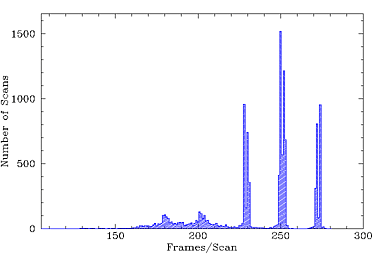 |
| Figure 2 - Histogram showing the distribution of
the number of frames acquired per scan during all phases of the WISE survey. |
Last update: 22 November 2013











